Vertigo & Imbalance
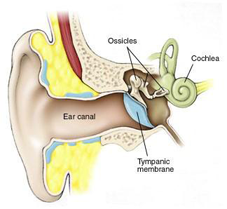
Vertigo is a type of dizziness, where there is a feeling of motion when one is stationary. The symptoms are due to a dysfunction of the vestibular system in the inner ear. It is often associated with nausea and vomiting as well as difficulties standing or walking.
There are three types of vertigo:
- objective- subjects, are moving around the patient
- subjective- patient feels as if moving himself
- pseudovertigo- intensive sensation of rotation inside the patient's head.
The most common causes are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, concussion and vestibular migraine while less common causes include Ménière's disease and vestibular neuritis and excessive consumption of alcohol. Central nervous system disorders can cause vertigo and the symptoms include multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, neck injuries, certain forms of migraine, acoustic neuroma, cerebellar and brain stem tumors.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. A complete medical evaluation is recommended for anyone with vertigo and imbalance. This can reveal the true cause and suggest one or more solutions based upon treating the underlying disorder.
 Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's Disease